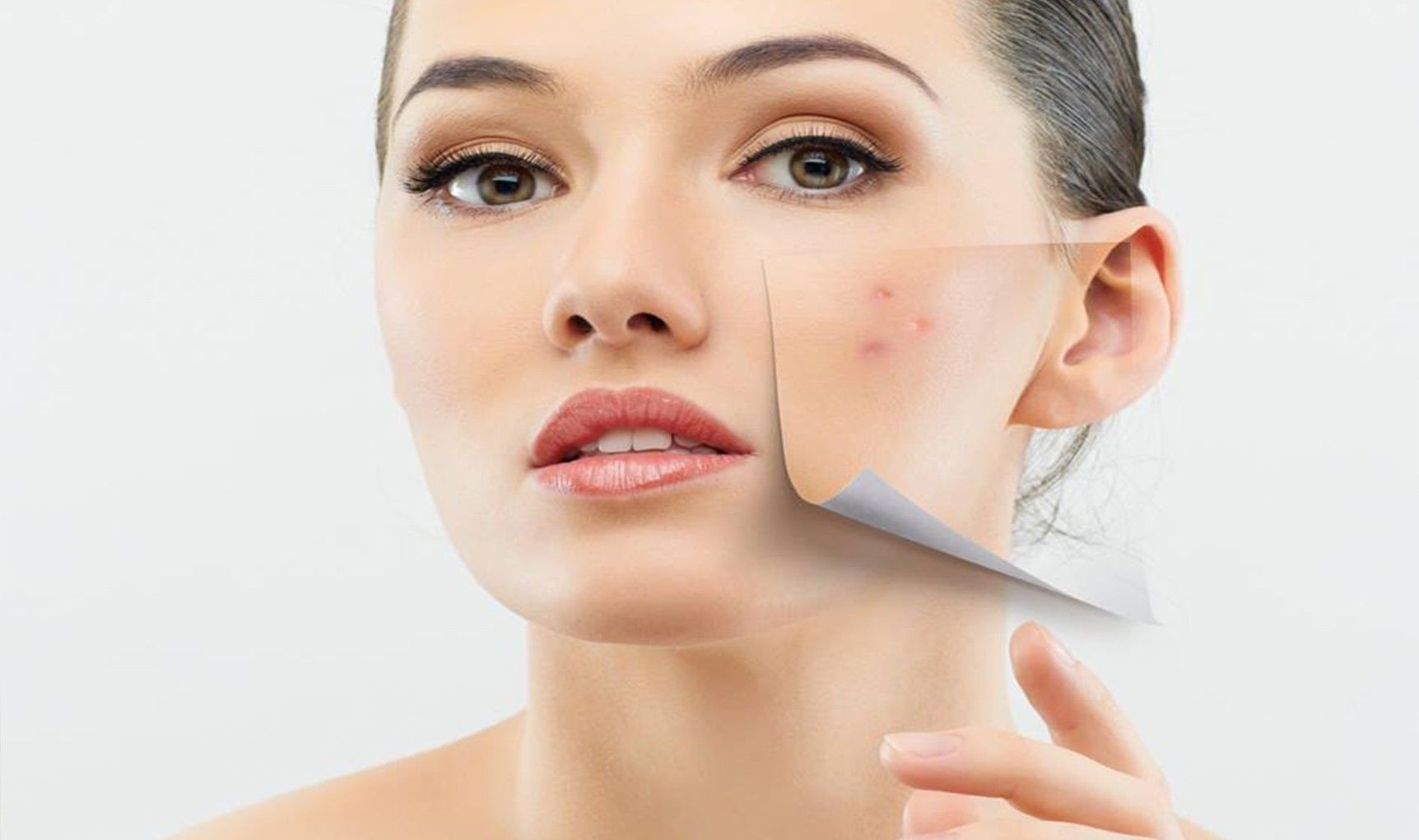
New Drugs in Dermatology
August 25, 2019
FDA Approved Drugs for Ophthalmology
August 25, 2019Drugs Commonly Used in Urology
There are numerous drugs used in urology, the medical specialty which deals with diseases of the male and female urinary tract as well as the male reproductive system. The drugs can be broken down by their mechanism of action and the biological function they target.
The most commonly prescribed classes of drugs in urology include:
Alpha blockers which work by relaxing muscles at the bladder neck to improve urinary flow
5-alpha inhibitors which block the production of a specific male hormone associated with prostate enlargement
Anticholinergics which minimize bladder contractions and increase bladder capacity for people with an overactive bladder
The drugs can be used on their own or in combination therapy. Some pharmaceutical companies have also created two-in-one drugs like Duodart which combines an alpha-blocker with a 5-alpha inhibitor.
Alpha Blockers
Alpha blockers, also called alpha-adrenergic antagonists, are used in urology to treat the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland (known as benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH). They do so by preventing the hormone norepinephrine from constricting certain smooth muscles and blood vessels. By doing so, the drug can improve urinary flow in older men with prostate problems.
Alpha blockers currently approved for the treatment of BPH include:
Cardura or Cardura XL (doxazosin)
Flomax (tamsulosin)
Hydrin (terazosin)
Uroxatral (alfuzosin)
Some alpha blockers are available in short- and long-acting formulations. The short-acting drugs work quickly, but their effects only last a few hours. Long-acting versions may take longer to work, but their effects last longer. The choice of formulation is largely dependent on the severity of the BPH.
Broadly speaking, alpha blockers may cause dizziness, headaches, postural hypotension (low blood pressure when you stand), or retrograde ejaculation (a condition where semen is ejaculated into the bladder).
5-Alpha Inhibitors
5-alpha inhibitors, also known as 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, work by preventing the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone, the hormone associated with both BPH and male pattern baldness. 5-alpha inhibitors are prescribed for the chronic treatment of BPH and may take up to six months before the effects are fully felt.
5-alpha inhibitors currently approved for the treatment of BPH are:
Avodart (dutasteride)
Propecia or Proscar (low- and high-dose finasteride, respectively)
As a drug class, 5-alpha inhibitors may cause the loss of libido, impotence, or retrograde ejaculation.
Anticholinergics
Anticholinergic drugs work blocking the action of a chemical neurotransmitter, known as acetylcholine, which sends signals to the brain that trigger abnormal bladder contractions. By doing so, the drug can reduce the symptoms of overactive bladder in which people feel as if they need to urinate even when the bladder isn’t full.
Among the anticholinergics currently approved for the treatment of overactive bladder are:
Detrol (tolterodine)
Enablex (darifenacin)
Oxytrol or Ditropan XL (oxybutynin)
Regurin and Sanctura (trospium chloride)
Toviaz (fesoterodine)
Vesicare (solifenacin)
Anticholinergics may cause dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, and rapid heartbeat (tachycardia).
Other Drugs Used in Urology
As a specialty encompassing both the urinary and male reproductive tract, urologists rely on an armory of medications to treat conditions as far-ranging as prostate cancer, urinary tract infections (UTIs), erectile dysfunction (ED), hypogonadism (low production of testosterone), and Peyronie’s disease (a condition characterized by a curved, painful erection).